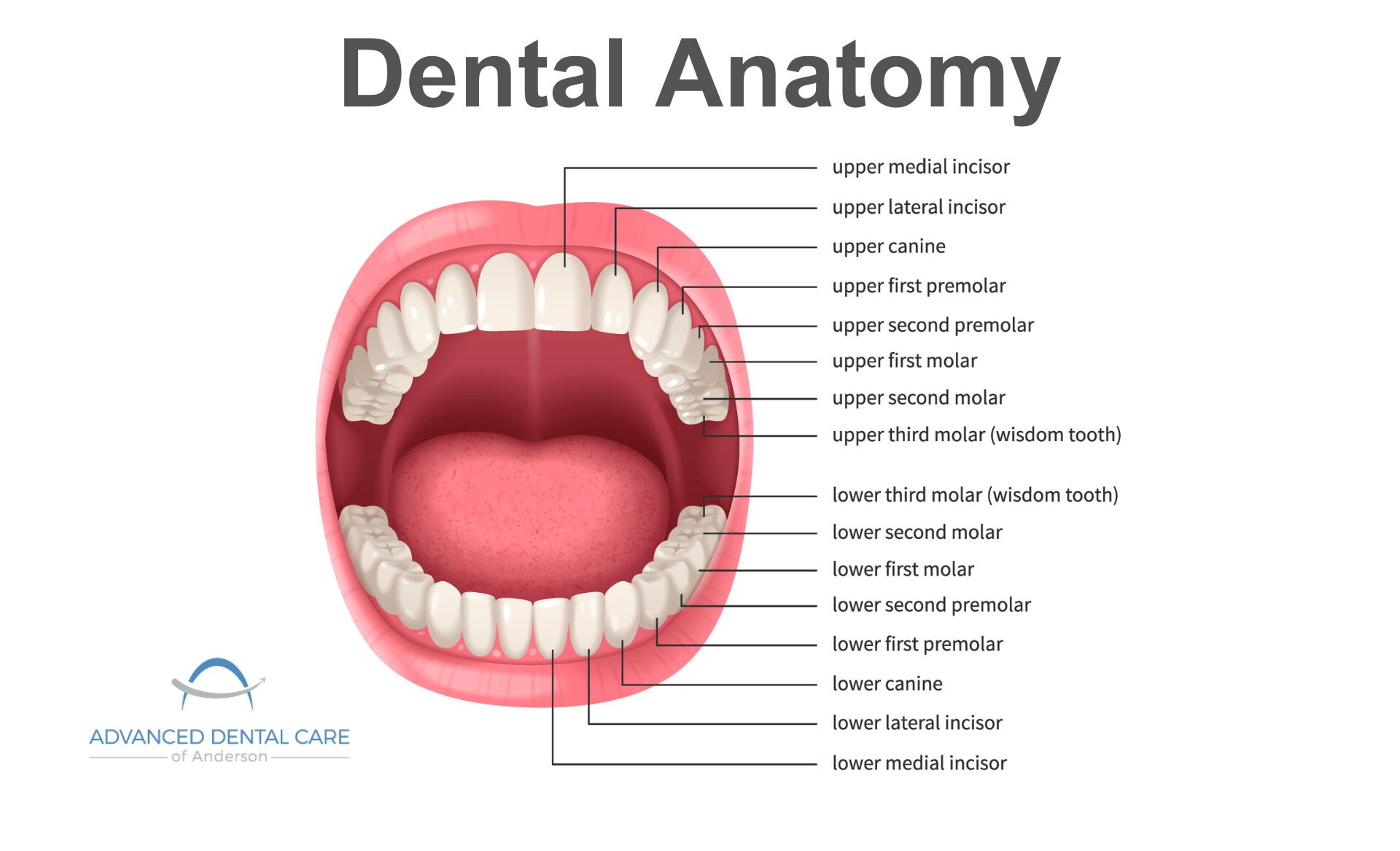
Wondering how many teeth do adults have? The typical number is 32, including wisdom teeth. But this can vary. Authored by Advanced Dental Care of Indiana, this article aims to explain the various types of teeth, their functions, and the reasons behind variations in tooth count.
Key Takeaways
- Adults typically have 32 permanent teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, each serving distinct functions crucial for oral health.
- Wisdom teeth can affect the total count of adult teeth, with potential complications necessitating removal; variations in tooth count can arise due to genetics, trauma, or dental issues.
- Maintaining healthy teeth involves good oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and understanding the importance of dental care during the transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth.
Total Count of Adult Teeth
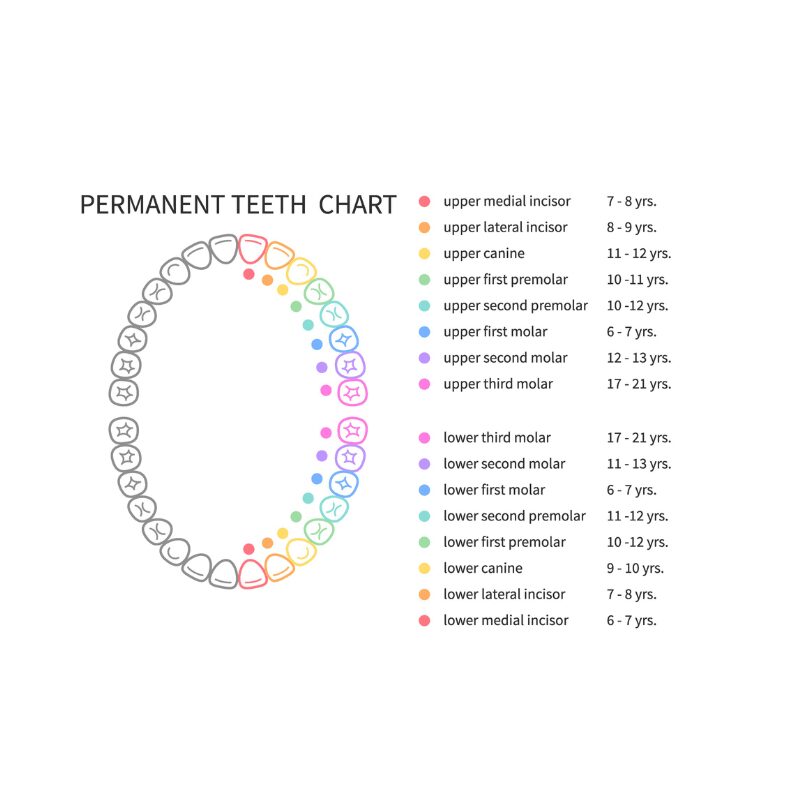
The average adult possesses 32 permanent teeth. This is the typical count for fully developed permanent dentition. This count includes the often troublesome wisdom teeth, which are part of the 32 teeth. Your full set of adult teeth plays a crucial role in effective chewing and overall oral health. These teeth are designed to work together, ensuring you can break down food efficiently, which is vital for digestion and nutrient absorption.
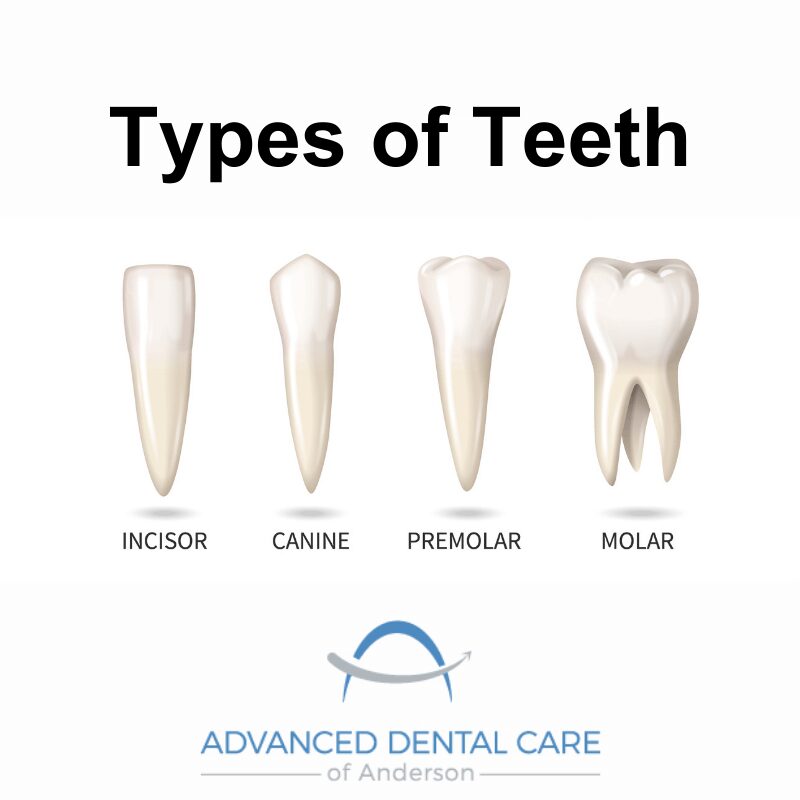
The standard 32 teeth in adults include four types:
- Incisors: cut food
- Canines: tear
- Premolars: crush
- Molars: grind Each type has a specific function, contributing to the overall health and efficiency of your mouth.
This diversity in teeth function highlights the importance of having a complete set of teeth. Missing teeth can lead to various issues, including difficulty in chewing, misalignment of remaining teeth, and even changes in facial structure.
Upper and Lower Jaw Teeth Count
The human body mouth is a marvel of symmetry. Adults typically have a total of 32 teeth, with an equal distribution in both the upper and lower jaws. This arrangement ensures that both human teeth jaws work together harmoniously to facilitate effective chewing and speaking.
The upper jaw, or maxilla, contains 16 teeth, which include: Incisors, Canines, Premolars, and Molars.
Likewise, the lower jaw, or mandible, also comprises 16 teeth mirroring the structure of the upper jaw. This balance is crucial for maintaining proper alignment and function of the mouth.
The combined total of teeth in the upper and lower jaws for adults is 32, perfectly designed to handle the varied tasks our teeth perform every day.
Upper Jaw (Top Teeth)
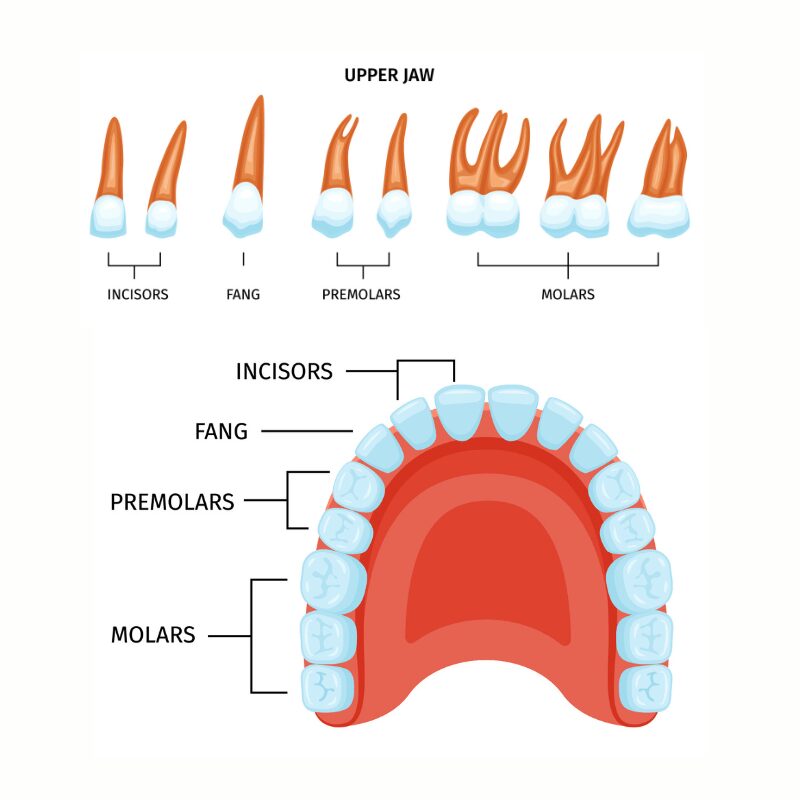
Upper Jaw (Top Teeth)
The upper jaw, home to 16 teeth, contains the following types of certain teeth, each positioned to perform different functions:
- Incisors: Four at the front, designed to cut food, essential for the initial stage of digestion.
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Next, we have the canines, also known as pointed teeth, which are perfect for tearing into tear food like meat and crunchy vegetables. Following the canines are the premolars and molars, which help tear, crush, and grind food into smaller pieces.
The upper jaw’s arrangement ensures that each type of tooth can perform its function effectively, contributing to overall oral health, including the upper right third molar.
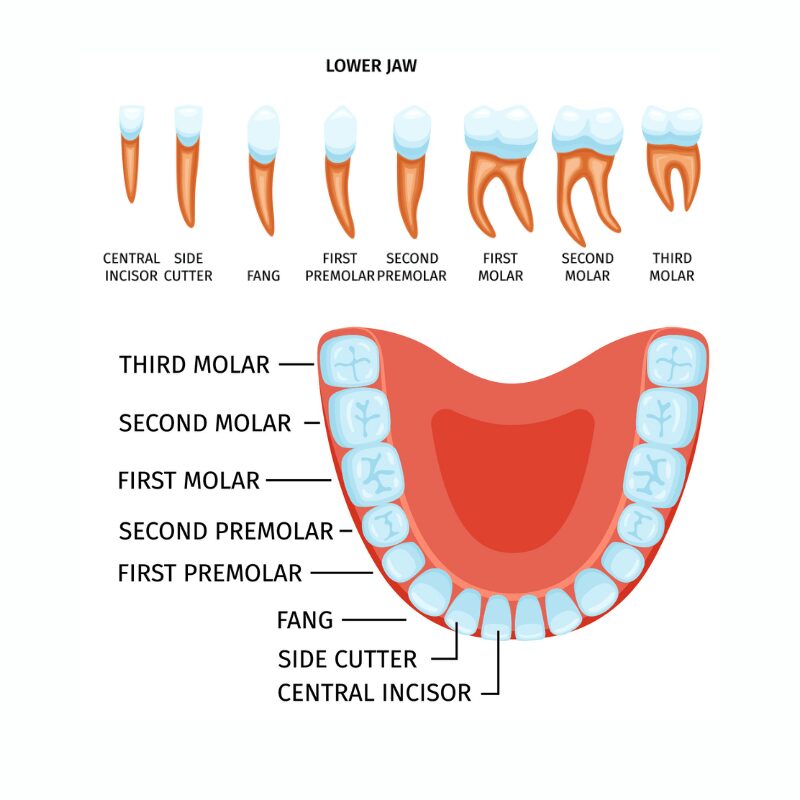
Lower Jaw (Bottom Teeth)
The lower jaw also contains 16 teeth, mirroring the structure and function of the upper jaw. This symmetrical design is crucial for balanced chewing and overall dental harmony. The incisors and canines in the lower jaw perform similar functions to those in the upper jaw, cutting and tearing food.
The molar teeth in the lower teeth are particularly important for grinding food into smaller, digestible pieces. If wisdom teeth are removed, there are usually eight molars remaining in the lower jaw, including the lower left third molar. This arrangement ensures that the lower jaw can effectively complement the upper jaw, creating a well-coordinated system for processing food.
Wisdom Teeth: Impact on Total Teeth Count
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, usually start to appear during the ages of 17 to 25. This timeframe is when most individuals experience their development. Their arrival can increase the total number of adult teeth to 32. However, not everyone develops wisdom teeth; study suggests 20 – 25% of people never do. For those who do, wisdom teeth can either be a blessing or a curse.
If wisdom teeth are removed, the total count of adult teeth drops to 28. The decision to have wisdom teeth removed often depends on whether they cause problems. These teeth can sometimes become impacted, leading to pain, infection, and other complications.
Understanding the role and potential issues of wisdom teeth is crucial for managing your dental health effectively.
Wisdom Teeth Complications
Wisdom teeth can sometimes cause significant complications. They often don’t have enough room to emerge properly, leading to crowding, pain, and infection. These issues can disrupt the alignment of other teeth, making them harder to clean and maintain.
Due to these potential complications, dental professionals often recommend the removal of wisdom teeth. This preventive measure can help avoid more severe problems down the line, such as gum disease and damage to adjacent teeth. Early assessment and timely removal of problematic wisdom teeth can significantly contribute to maintaining overall oral health.
Variations in Adult Teeth Count
While most adults have 32 teeth, variations in the total count are not uncommon. On average, individuals aged 20 to 64 have about 25.5 remaining adult teeth. Factors such as age, genetics, trauma, and dental extractions can influence the number of teeth an adult has.
Conditions such as congenital issues and the removal of wisdom teeth can lead to having fewer than 32 teeth. Common causes of adult tooth loss include:
- Trauma
- Gum disease
- Tooth decay
- Poor hygiene
- Smoking
Understanding these variations helps in appreciating the unique dental landscape each person may have.
Conditions Leading to More or Fewer Teeth
Several conditions can affect teeth the number of teeth an individual has, including many teeth:
- Hyperdontia: having too many teeth than the typical count.
- Hypodontia: characterized by the congenital absence of one or more teeth.
- Oligodontia: involves the absence of six or more teeth at birth.
These conditions can significantly impact dental health and require specialized care, especially in cases of periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups and personalized treatment plans are essential for managing these unique dental conditions effectively. By understanding the causes and implications of these variations, individuals can better manage their oral health.
Baby Teeth vs. Adult Teeth
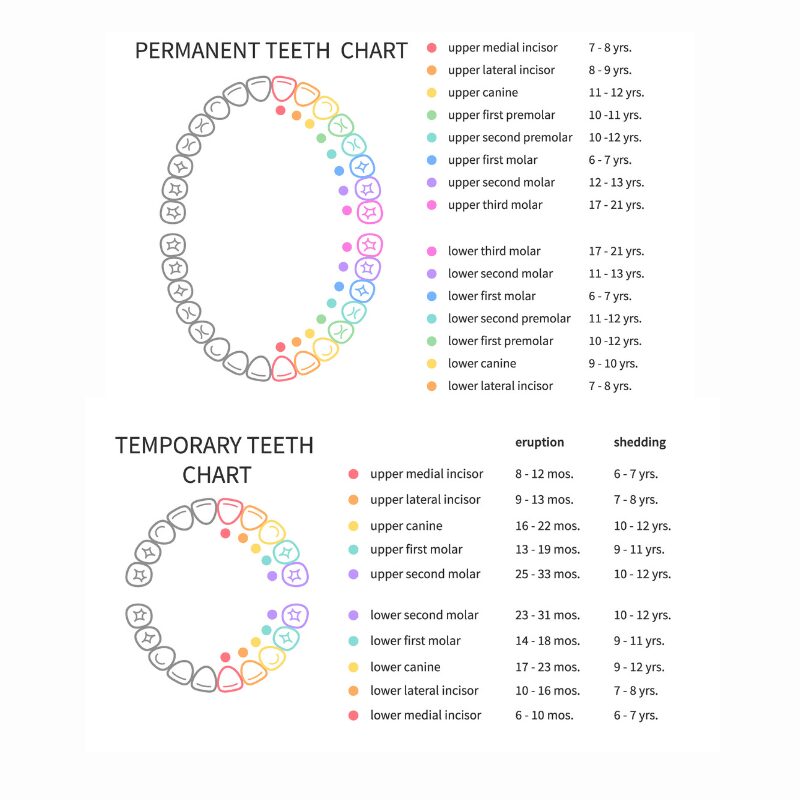
Baby teeth, also known as primary or deciduous teeth, differ significantly from adult teeth. A complete set of baby teeth consists of 20 individual teeth. These teeth are crucial for a child’s development, aiding in chewing, speaking, and maintaining space for future permanent teeth.
An adult typically has 32 permanent teeth, which include: how many teeth – eight incisors, 4 canine teeth, eight premolars, and 8 or 12 molars.
The transition from baby teeth to adult teeth is a vital process that ensures the development of a healthy, functional set of teeth, including milk teeth. Understanding these differences highlights the importance of proper dental care from an early age, which is why consulting with baby teeth dentists can be beneficial.
Transition from Baby Teeth to Permanent Teeth
The process of shedding baby teeth generally starts around age 6. This transition is a significant milestone in a child’s development. The first type of permanent teeth to come in after losing primary teeth is usually the molars.
Permanent teeth begin to emerge after primary teeth are lost, typically starting with molars. This process continues until around the age of 12, when most children have their full set of first permanent teeth, adult teeth, and permanent adult teeth. Proper dental care during this transition is crucial to ensure the health and alignment of the new permanent teeth.
Maintaining Healthy Teeth
Dentists at Advanced Dental Care of Indiana suggest maintaining healthy teeth is essential for overall well-being. Good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, are crucial for preventing tooth decay and gum disease. Using fluoride toothpaste strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities.
Regular dental visits are also important for preventing and addressing dental issues. These practices lead to improved dental health and the longevity of teeth. Implementing a thorough dental care routine can significantly enhance your oral health and overall quality of life.
Daily Dental Care Routine
A daily dental care routine is the foundation of good oral health. Brushing should be done twice daily using fluoride toothpaste, which helps strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities. Daily brushing is essential for eliminating plaque and preventing decay and gum disease.
Flossing daily is equally important as it cleans areas that brushing cannot reach, removing plaque and food particles from between teeth. Using dental floss and an antibacterial mouthwash can further enhance dental hygiene by controlling harmful oral bacteria.
Consistently following these practices is key to maintaining a healthy mouth and preventing dental issues.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are vital for maintaining oral health. Dental cleanings help prevent cavities and gum disease by removing tartar that cannot be eliminated by brushing and flossing alone. Routine dental exams allow early detection of potential oral health problems.
At least twice a year, individuals should visit the dentist for cleanings and screenings. Those prone to dental issues may require more frequent visits. Professional cleanings and regular check-ups ensure that any dental problems are addressed early, maintaining the health and longevity of your teeth.
Ready to take your oral health to the next level? Trust Advanced Dental Care of Indiana for expert, compassionate dental services tailored to your needs. Schedule your appointment today and experience the difference of personalized, advanced dental care that keeps your smile healthy and bright for years to come!
Tooth Loss and Replacement Options
Tooth loss can occur due to various factors such as gum disease, tooth decay, and trauma. It can significantly impact oral health and overall quality of life. Fortunately, there are several options available for replacing lost teeth.
Dental implants are a popular choice as they provide a permanent solution. There are many teeth replacement options, including dentures, available in partial or complete forms, which offer a removable option for tooth replacement. Many teeth replacement options include bridges, connecting artificial teeth to adjacent natural teeth.
In some cases, bone grafting may be necessary before implant placement if there is insufficient jawbone. These options ensure that individuals can maintain their dental function and appearance despite tooth loss.
Summary
Understanding the structure and care of adult teeth is essential for maintaining a healthy smile. Most adults have 32 permanent teeth, which include wisdom teeth. The distribution of teeth in the upper and lower jaws ensures balanced function and effective chewing. Wisdom teeth can impact the total count, often leading to removal due to complications.
Variations in adult teeth count can occur due to several factors, including genetics and health conditions. The transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth is a critical period requiring proper care. Maintaining healthy teeth through daily care and regular check-ups is vital for preventing dental issues. For those who experience tooth loss, various replacement options are available to restore dental function and aesthetics.
For personalized dental care that keeps your smile healthy and bright, contact Advanced Dental Care of Indiana today. Our experienced team is dedicated to providing comprehensive services tailored to your unique needs. Don’t wait—schedule your appointment now and experience expert care that puts your oral health first!
📞 Call now to book your appointment:
- Anderson: (765) 622-7000
- Fortville: (317) 485-7000
- Indianapolis: (317) 926-5200
Frequently Asked Questions
Maintaining a daily dental care routine is crucial for preventing tooth decay and gum disease, thereby promoting overall oral health. Consistent care safeguards your smile and enhances your well-being.
Hyperdontia is a dental condition characterized by the presence of extra teeth beyond the normal count. It can lead to complications such as crowding and misalignment of the remaining teeth.
Wisdom teeth usually emerge between the ages of 17 and 25. Therefore, if you are within this age range, it may be advisable to monitor their development.
The main types of teeth in the upper jaw are incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each type serves a specific function in the process of chewing and breaking down food.
Human adults typically have a total of 32 permanent teeth, which includes the wisdom teeth.